Unit 14: Interference & Beat Frequency
Practice Problems

Note: problem difficulty is ranked using a star system.
(*) One-star problems are fundamental to the unit, and can be done relatively quickly. Use these problems to introduce yourself to the material.
(**) Two-star problems are more difficult, and require an understanding of one or two key concepts. Use these problems to test your understanding of the material.
(***) Three-star problems are the most difficult, and require some creative thinking in addition to a deep familiarity with multiple key concepts. Use these problems to challenge yourself; if you can complete one of these, you’re on your way to mastering the material.
*Q14.1) Explain the difference between constructive and destructive interference, and how this relates to the idea of “active noise-cancellation” headphone technology.
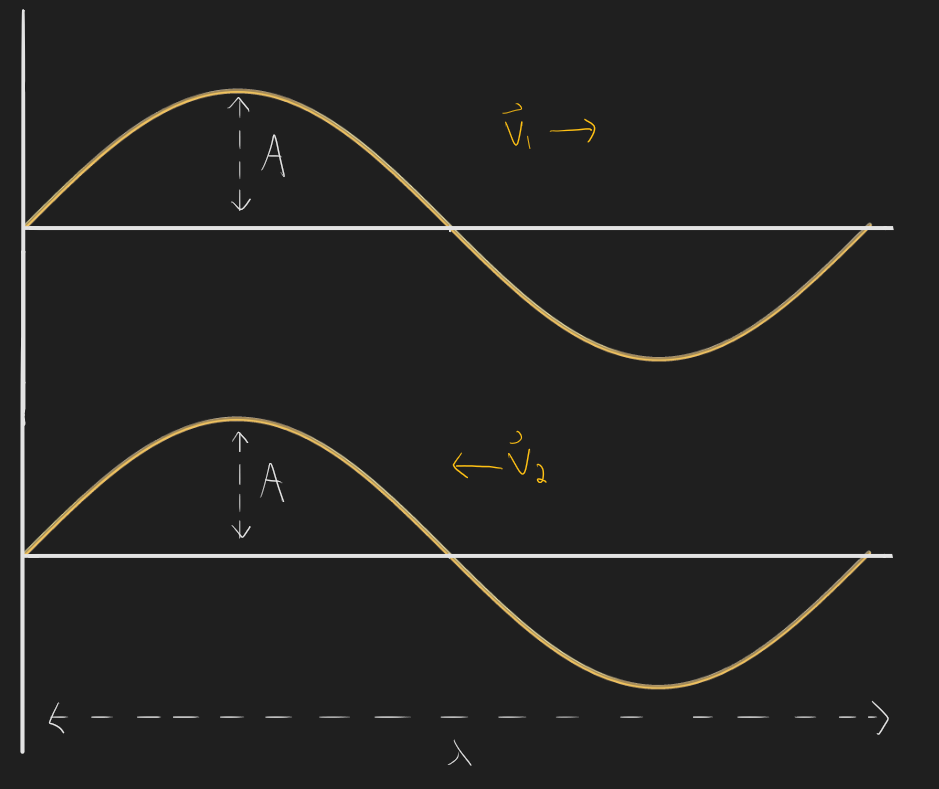
*Q14.2) The following is a snapshot in time of two travelling waves, taken at t = 0. The two waves have identical amplitude, wavelength, and frequency, but are moving in opposite directions. Sketch the resulting wave if the two waves were to overlap at the instant in time shown below (t = 0).
**Q14.3) Consider again the waves from Q14.2. Suppose you were to wait a length of time equal to a quarter period (t = T/4) and take another snapshot of the two waves.
a) Sketch the two waves at the new instant in time (t = T/4).
b) Sketch the resulting wave if the two waves were to interfere at t = T/4.
c) Sketch the resulting wave if the two waves were to interfere after waiting a half period (at t = T/2).
*Q14.4) A piano tuner strikes a 740Hz tuning fork while simultaneously pressing on the G key of a piano, and counts 24 beats in 8 seconds. What are the possible frequencies of the piano string?
***Q14.5) In an attempt to tune your guitar, you strike a 110Hz tuning fork and simultaneously pluck the A-string. While listening to the two tones overlapping, you count 4 beats every second.
a) What are the possible frequencies of the A-string?
b) You slightly increase the tension in the A-string and notice that the beat frequency increases. What then must have been the original frequency of the A-string?
c) What was the original wavelength of the A-string?